What is Employee Salary Slip?
A salary slip or a pay slip is a legal document provided by an employer to its employees. It contains a thorough breakdown of the employee's salary, including earnings, deductions, and other relevant information for a specific time period.
Salary slips can be in the form of a hard copy or emailed to the employees in a pdf format on the respective organization’s salary portals which they can later view or print.
Components of an Employee Salary Slip
In this section, we will gain more clarity about the different components of an employee salary slip. Helping you understand the key elements that contribute to your financial compensation. :-
1. Earnings
Basic Salary: This is the most essential component of your salary, accounting for up to 35 - 40% of your total pay. It is completely taxable and also acts as a foundation for calculating the other aspects of pay.
Dearness Allowance (DA): It is a percentage of your base pay that is granted to help offset the effects of inflation, it is fully taxable.
House Rent Allowance (HRA): This is an allowance to assist people in paying their rent. The amount of HRA varies by location and ranges from 40 to 50 percent of base pay. HRA can help you save money on taxes.
According to rule 2A under Section 10 (13A), the one which amounts the least is exempted -
- Actual HRA received from the employer
- For people living in metro cities: 50% of Basic salary + Dearness allowance; non-metro cities: 40% of Basic salary + Dearness allowance
- Actual rent paid minus 10% of Basic salary + Dearness allowance
Conveyance & Medical Allowance: Conveyance allowance is provided to an employee for covering expenditure incurred on the commute to the office.
Medical allowance is the amount of money given to cover the medical expenses of an employee.
Employees are eligible for a standard deduction of up to ₹50,000 of conveyance & medical allowance for the financial year 2023-2024.
Performance and Special Allowances: Employees are offered performance and special allowances to motivate them to perform better. This component is entirely taxed.
Leave Travel Allowance: LTA is a provision designed to cover the travel expenses incurred by employees and their immediate family members.
This allowance, provided by the employer, offers an income tax exemption on the actual travel costs. For example, the leave travel allowance provided is ₹25,000 but the expenses were ₹20,000. The exempted amount would be ₹20,000
To claim this deduction, employees are required to submit proof of their journey.
However, there are certain restrictions to keep in mind. The LTA exemption is available for two journeys in a block of four calendar years.
Other Allowances: This category includes all of an employer's additional allowances that the company may allow to its employees. Such allowances can be grouped as "Other Allowances'' by an employer.
2. Deductions
EPF (Employees Provident Fund): This is a mandatory deduction from your paycheck and an accumulation of funds for your retirement.
This portion of your employee salary slip represents at least 12% of your basic pay and is deposited into an EPF account.
Notably, under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act, your payment to the EPF up to a certain amount is tax-free.
Professional Tax: It is imposed on all individuals with an income, including salaried workers, professionals, and traders.
However, it is only imposed in a few states, which are Karnataka, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Gujarat, Assam, Chhattisgarh, Kerala, Meghalaya, Orissa, Tripura, Jharkhand, Bihar, and Madhya Pradesh.
It is determined according to a person's tax bracket and could range from ₹200 and ₹2,500
TDS (Tax Deductible at Source): TDS is the amount of tax deducted by your employer on behalf of the Income Tax Department.
It is determined by the employee's gross tax bracket.
This cost can be reduced by investing in tax-saving investments such as equity mutual funds (ELSS), PPF, NPS, and tax-saving FDs and providing your employer with the necessary papers.
What is the difference between CTC & In-hand Salary?
Cost to the Company (CTC) represents the total expenditure an employer incurs on an employee during his hiring process. This comprehensive amount comprises multiple elements including earnings from base salary, various allowances, deductions for EPF and taxes, etc.
Whereas, gross salary represents the total income of an employee before any deductions are made like EPF & taxes.
After all applicable deductions from the gross salary, including taxes, what remains is the net pay or net salary. This is also commonly referred to as the take-home or in-hand salary, as it's the actual amount received by the employee.
Want to know how your CTC translates into in-hand salary after a raise? Try our free salary hike calculator to see what your next pay slip could look like.
But why is this Salary Slip so important for Employees?
Do you know companies are legally bound to issue you your salary slip with a detailed breakdown? So clearly these pay-slips hold some real importance. Here’s why:
Proof of employment: Your salary slip acts as proof of employment in eyes of the law.
If you’re applying for a visa or executive program at various colleges, they might even ask you to produce copies of your pay-slip as proof of your latest drawn salary and designation.
Income Tax Planning: Your salary is made up of numerous components - basic income, the HRA, the transportation allowance, the medical allowance, the leave travel allowance, and so on.
And they are all taxed differently. So knowing how to read a employee salary slip and understand its components is only beneficial. So knowing how to read your salary slip and understanding its components can help you while filing your income tax return.
To get a loan or a credit card: Banks ask for your salary pay slip (because it contains all information about your monthly income) as a vital component in determining your ability to pay back your debts.
Hence, your salary slip, again, is a crucial document when applying for a credit card, loan, mortgage, or other type of loan.
For finding a new job: When switching jobs, a salary slip can help you choose positions wisely from several companies.
It also functions as a negotiator for a raise in pay when switching jobs. In fact, many companies even ask you to attach your previous salary slip during the onboarding process.
For a better understanding: Your employee salary slip contains components that are mandatory savings in a way.
Like, EPF and ESI. You can choose to opt out of some of these mandatory savings and put your money into high-yielding investments.
Hence, understanding the salary slip and its components might assist you in taking advantage of the positions you find yourself in and spend your salary effectively.
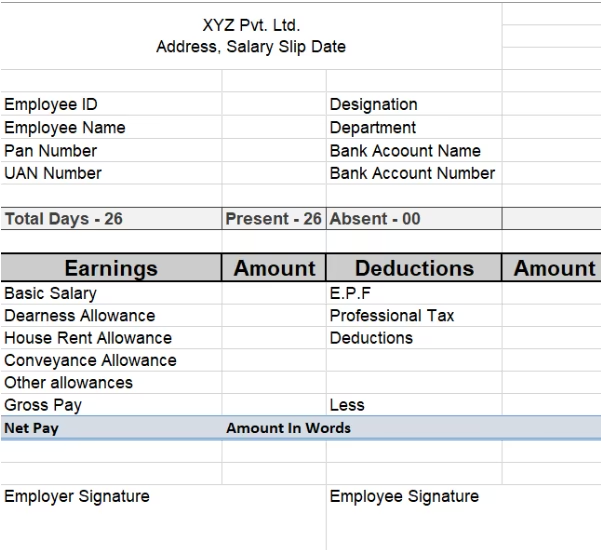
Employee Salary Slip Format
If you are wondering how to make your salary slip, here's a sample format for employee salary slip you can follow
- Company name, address, Salary slip date
- Employee name, code, designation, and department
- Employee PAN/Aadhaar number, bank name, and account number
- EPF account number and UAN (Universal Account Number)
- Total Number Of Working days, number of days present and leaves
- A list of all the earnings and deduction
- Gross and Net pay in numbers and words
Employee Salary Slip Template
Download Salary Slip Template Here
Final Words
There you have it, your mini-guide to your employee salary slip. Now the next time you get your employee pay slip, you know what you have to do. Read it, understand it, and check if you can save any taxes anywhere.
Now, as you have understood all aspects of an employee salary slips we hope it will also help you to make better decisions with your savings plans. You can always save while you spend using Jar App, which not only helps you to save money, but it also invests in Digital Gold.